Tips for Using Laser Machines to Cut Steel Plates

Using a laser cutting machine to cut steel plates has revolutionized the way industries approach metal fabrication. You can achieve unmatched precision and efficiency, making it easier to handle even the most intricate designs. Laser machines deliver consistent performance, ensuring every cut meets high-quality standards. This technology doesn’t just save time; it also reduces costs by minimizing material waste. Whether you’re working with carbon steel or stainless steel, laser cutting offers a reliable solution for superior results. Curious about what machine can laser cut steel plate? The answer lies in the advanced capabilities of modern laser systems.
Understanding Laser Cutting and Its Basics
Laser cutting has become a game-changer in the metal fabrication industry. It allows you to achieve precise cuts with minimal effort. But to get the best results, you need to understand the basics of how it works and what makes it so effective. Let’s dive into the essentials.
What Machine Can Laser Cut Steel Plate?
When it comes to cutting steel plates, not all machines are created equal. You need a machine specifically designed for this task. Fiber laser cutting machines, like those from DXTECH, are excellent choices. These machines combine advanced technology with reliable performance, making them ideal for cutting carbon steel and stainless steel plates. They offer adjustable parameters such as power, speed, and frequency, allowing you to tailor the settings to the thickness of the steel plate you’re working with.
Some models even integrate sheet and pipe cutting functions, which can save you time and reduce costs. If you’re wondering what machine can laser cut steel plate effectively, fiber laser machines are your answer. They deliver precision and efficiency, ensuring clean cuts every time.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting uses a high-powered laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material. The process starts with the laser source generating a focused beam of light. This beam is directed through a cutting head and nozzle, which concentrates the energy onto a specific point on the steel plate. The intense heat melts the material, while assist gases like oxygen or nitrogen blow away the molten metal, leaving a clean edge.
The entire process is controlled by a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system. This system ensures that the laser follows the exact path of your design, making it possible to create intricate patterns and shapes with ease. By adjusting the laser’s power and speed, you can cut through various steel thicknesses without compromising quality.
Key Components of a Laser Cutting Machine
To fully understand laser cutting, you need to know the key components of a laser cutting machine. Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and high-quality results.
Laser Source
The laser source is the heart of the machine. It generates the high-energy beam used for cutting. Fiber lasers are particularly popular because they offer excellent beam quality and energy efficiency. They are also versatile, capable of cutting different types of steel with precision.
Cutting Head and Nozzle
The cutting head houses the lens and nozzle, which focus the laser beam onto the steel plate. A shorter focal length lens can achieve a tighter focus, making it ideal for cutting carbon steel. The nozzle also directs assist gases to the cutting area, helping to remove debris and improve cut quality.
CNC Controller
The CNC controller acts as the brain of the machine. It translates your design file into precise movements, guiding the laser along the desired cutting path. This ensures accuracy and consistency, even for complex designs. With the right software, you can optimize cutting paths to save time and reduce material waste.
By understanding these components and how they work together, you can maximize the performance of your laser cutting machine. Whether you’re cutting thin sheets or thick plates, knowing the basics will help you achieve the best results.
Safety Guidelines for Laser Cutting
Operating laser machines for cutting steel plates can be incredibly efficient, but safety should always come first. By following proper safety guidelines, you can protect yourself and others while ensuring smooth operations. Let’s explore the key aspects of staying safe during sheet metal laser cutting.
Importance of Safety in Sheet Metal Laser Cutting
Sheet metal laser cutting involves high-powered lasers, which can pose risks if not handled correctly. The intense heat generated during the process can lead to burns or fires. Additionally, the particles formed during cutting may include ultrafine agglomerates that could affect air quality. Studies have shown that these particles vary depending on the type of metal and laser used. While occupational exposure levels are generally low, open laser cutters may increase the risk of inhaling harmful particles. Prioritizing safety minimizes these risks and ensures a healthier work environment.
Essential Safety Precautions
Taking the right precautions can make all the difference when working with laser cutting machines. Here are some essential steps to follow:
Wearing Protective Gear
Always wear appropriate protective gear. Safety goggles shield your eyes from the laser beam and any stray sparks. Heat-resistant gloves protect your hands from burns. A face mask or respirator helps reduce exposure to fine particles released during cutting. These simple measures can significantly lower the chances of injury.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Good ventilation is crucial during sheet metal laser cutting. The process releases fumes and particles that can accumulate in the air. Proper airflow helps dissipate heat and removes smoke, improving visibility and air quality. Install an exhaust system or use air filtration units to maintain a safe workspace.
Avoiding Direct Laser Exposure
Never look directly at the laser beam or expose your skin to it. Even brief contact can cause severe damage. Always ensure the laser cutting machine is enclosed or equipped with safety barriers. If you need to inspect the machine, turn it off first to avoid accidental exposure.
Workplace Safety Tips
A clean and organized workspace contributes to both safety and efficiency. Follow these tips to maintain a secure environment:
Keeping the Work Area Clean
Clutter in the work area can lead to accidents. Remove unnecessary tools, materials, and debris before starting the cutting process. A clean space reduces the risk of fires caused by stray sparks or heat.
Emergency Stop Procedures
Familiarize yourself with the machine’s emergency stop button. In case of a malfunction or unexpected situation, you’ll need to act quickly. Knowing how to shut down the machine immediately can prevent injuries and equipment damage.
By adhering to these safety guidelines, you can create a safer and more productive environment for laser cutting. Remember, taking precautions not only protects you but also ensures the longevity of your equipment and the quality of your work.
Selecting the Right Steel Material for Laser Cutting
Choosing the right steel material is crucial for achieving precise and efficient results with laser cutting. The type of steel you select directly impacts the quality of your cuts, the machine's performance, and the overall success of your project. Let’s explore the best options and factors to consider.
Types of Steel Suitable for Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Not all steel types are equally suited for laser cutting. Some materials perform better due to their composition and properties. Here are the top choices:
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is one of the most popular materials for laser cutting. Its affordability and versatility make it a go-to option for many projects. When cutting carbon steel, you’ll notice that it responds well to the laser’s heat, allowing for clean and precise cuts. This material is ideal for applications requiring durability and strength, such as construction and automotive parts.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel stands out for its corrosion resistance and polished finish. It’s an excellent choice for projects where aesthetics and longevity matter. Laser machines handle stainless steel effectively, producing smooth edges without compromising the material’s integrity. This makes it perfect for kitchen equipment, medical tools, and decorative items.
Alloy Steel
Alloy steel combines various elements like chromium, nickel, and manganese to enhance its properties. This type of steel offers improved strength, wear resistance, and toughness. Fiber laser cutting machines excel at processing alloy steel, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like machinery components and industrial tools.
Determining the Appropriate Thickness
The thickness of the steel plate plays a significant role in laser cutting. Thinner plates are easier to cut and require less laser power, resulting in faster processing times. For thicker plates, you’ll need to adjust the machine’s settings, such as reducing the cutting speed and increasing the laser’s power. This ensures the laser penetrates the material effectively without leaving slag or burn marks.
When working with mild steel, for example, you can achieve excellent results by selecting the right thickness for your project. Thinner sheets are ideal for intricate designs, while thicker plates are better for structural applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Steel
Selecting the right steel involves more than just picking a type or thickness. You need to evaluate several factors to ensure the material meets your project’s requirements:
- Project Requirements: Consider the purpose of your project. If you need a durable and cost-effective option, mild steel is a great choice. For corrosion resistance, stainless steel is better.
- Machine Compatibility: Ensure the steel you choose is compatible with your laser cutting machine. Fiber laser cutting machines are optimized for metals like carbon steel and stainless steel.
- Finish Quality: Think about the desired finish. If you want a polished look, stainless steel is ideal. For a more rugged appearance, carbon steel works well.
- Budget: Balance your material choice with your budget. Mild steel is affordable, while stainless steel and alloy steel may cost more but offer additional benefits.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the best steel material for your laser cutting project. This ensures not only high-quality results but also efficient use of your resources.
Machine Setup and Calibration for Effective Laser Cutting
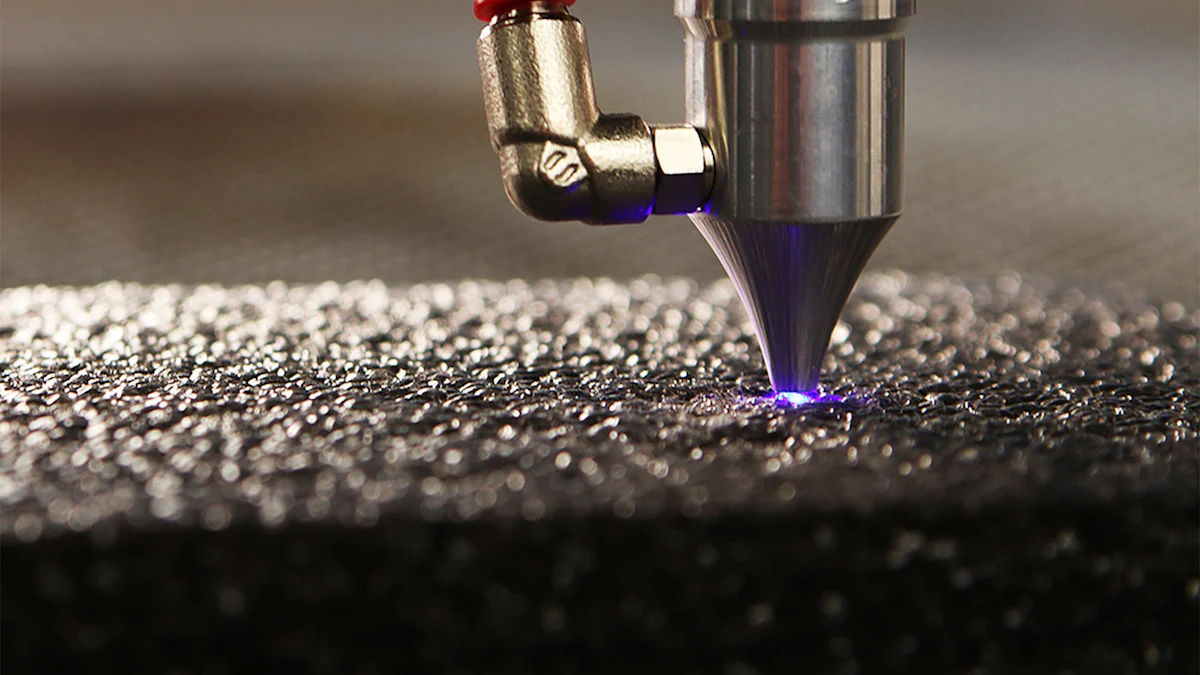

Setting up and calibrating your laser cutting machine properly is essential for achieving precise and efficient results. A well-prepared machine not only enhances performance but also ensures consistent quality in every cut. Let’s walk through the steps to get your machine ready for action.
Preparing the Laser Cutting Machine
Before you start cutting, you need to prepare your laser cutting machine. Proper preparation minimizes errors and extends the lifespan of your equipment.
Cleaning the Machine Components
Dirt and debris can interfere with the machine’s operation. Regularly clean all components, especially the cutting head and lenses. Dust or residue on these parts can scatter the laser beam, reducing its efficiency and accuracy. Use a soft, lint-free cloth and a cleaning solution designed for optical surfaces. Keeping the machine clean ensures smooth operation and better results.
Checking the Laser Optics
Inspect the laser optics to ensure they are in top condition. Scratches or smudges on the lens can distort the laser beam, affecting the quality of your cuts. Replace damaged lenses immediately. Also, check the alignment of the optics to ensure laser centering. Misaligned optics can lead to uneven cuts and wasted material. A quick inspection before each use can save you time and frustration later.
Calibrating the Machine for Accuracy
Calibration is crucial for maintaining the precision of your laser cutting machine. Accurate calibration ensures that the laser beam hits the material exactly where it should.
Aligning the Laser Beam
Start by aligning the laser beam. This step ensures that the beam travels straight and hits the cutting point accurately. Use the machine’s alignment tools to adjust the beam path. Misalignment can cause uneven cuts or damage to the material. Taking a few minutes to align the beam properly can make a big difference in the quality of your work.
Setting the Focus Point
The focus point determines how the laser interacts with the material. Adjust the focus so the beam is concentrated at the optimal distance from the steel plate. For most projects, this distance is between 0.010" and 0.020". Choosing the right nozzle can also help achieve a tighter focus, especially when working with carbon steel. Proper focus improves efficiency and reduces the risk of burn marks or slag.
Testing the Setup Before Cutting
Before you begin cutting, test the setup to ensure everything is working as it should. Run a trial cut on a scrap piece of steel. This allows you to check the machine’s settings and make adjustments if needed. Pay attention to the cut’s edges and depth. If you notice any inconsistencies, revisit the calibration steps. Testing saves you from costly mistakes and ensures your project starts on the right foot.
By following these steps, you can prepare your laser machines for optimal performance. Whether you’re cutting thin sheets or thick plates, proper setup and calibration are key to achieving high-quality results. Take the time to get it right, and you’ll see the difference in your work.
Optimizing Cutting Parameters for Steel Plates
Fine-tuning the cutting parameters is essential to achieve precise and efficient results when working with steel plates. By adjusting laser power, selecting the right assist gas, and managing cutting depth, you can significantly enhance the performance of your laser machines. Let’s explore how to optimize these factors for the best outcomes.
Adjusting Laser Power and Speed
Laser power and cutting speed are the two most critical factors in laser cutting. The right combination ensures clean cuts and minimizes defects. Start by setting the laser power according to the thickness of the steel plate. For thinner plates, lower power levels work well, while thicker plates require higher power to penetrate effectively.
Cutting speed plays an equally important role. A faster cutting speed reduces processing time but may compromise the quality of the cut. Slower speeds allow the laser to focus more energy on the material, which is ideal for thicker steel or intricate designs. For example, when cutting carbon steel, slowing down the speed helps the laser penetrate better, reducing slag and improving edge quality.
Experimentation is key. Run test cuts on scrap material to find the optimal balance between laser power and cutting speed. This approach ensures you achieve both precision and efficiency in your work.
Selecting the Right Assist Gas
Assist gases play a vital role in laser cutting by removing molten material and improving cut quality. Choosing the right gas depends on your project’s requirements and the type of steel you’re working with.
Oxygen for Faster Cuts
Oxygen is an excellent choice when speed is your priority. It reacts with the steel during cutting, creating additional heat that accelerates the process. This makes it ideal for thicker plates or projects with tight deadlines. However, keep in mind that oxygen can leave a slight oxide layer on the cut edges, which may require additional cleaning if a polished finish is needed.
Nitrogen for Cleaner Edges
Nitrogen, on the other hand, is perfect for achieving clean, oxidation-free edges. It doesn’t react with the steel, which helps maintain the material’s original appearance. This makes nitrogen ideal for stainless steel or projects where aesthetics matter. While it may not match oxygen in cutting speed, the superior edge quality often outweighs the slower pace.
Managing Cutting Depth and Kerf Width
Cutting depth and kerf width are crucial for ensuring accuracy and material efficiency. The cutting depth determines how deeply the laser penetrates the steel, while the kerf width refers to the width of the cut made by the laser.
To manage cutting depth, adjust the focus point of the laser. Position the beam at the optimal distance from the material, typically between 0.010" and 0.020". This ensures the laser’s energy is concentrated where it’s needed most. For thicker plates, increase the laser power and slow down the cutting speed to achieve the desired depth without compromising quality.
Kerf width affects how much material is removed during cutting. A narrower kerf width minimizes waste and allows for more precise cuts. Use a shorter focal length lens to achieve a tighter focus, especially when working with carbon steel. Regularly inspect and clean the cutting head to maintain consistent kerf width and overall performance.
By mastering these cutting parameters, you can unlock the full potential of your laser machines. Whether you’re prioritizing speed, edge quality, or material efficiency, these adjustments will help you achieve outstanding results.
Design and File Preparation for Laser Cutting
Preparing your design files correctly is a crucial step in laser cutting. A well-prepared file ensures smooth operations, reduces errors, and delivers high-quality results. Let’s explore how to get your designs ready for laser cutting.
Importance of Clean Vector Files
Clean vector files are the backbone of successful laser cutting. These files guide the laser along precise paths, ensuring accurate cuts. A vector file uses mathematical equations to define shapes, making it ideal for the precision required in laser cutting. Formats like SVG, DXF, and AI are commonly used for this purpose.
When preparing your vector file, avoid unnecessary details or overlapping lines. These can confuse the laser and lead to errors. Simplify your design to focus on the essential elements. For instance, if you’re creating a stencil, ensure all lines connect properly to avoid weak points in the final cut.
"Laser cutting requires a digital 2D vector drawing. This can be thought of as the stencil or route that the laser will follow as it cuts the metal."
By keeping your vector files clean and straightforward, you’ll save time and achieve better results.
Tips for Designing Efficient Cutting Paths
Efficient cutting paths not only improve the quality of your cuts but also reduce material waste and processing time. Here are some practical tips to optimize your designs:
Minimizing Sharp Corners
Sharp corners can slow down the cutting process and strain the laser. The machine needs to pause and adjust its direction, which can create burn marks or uneven edges. To avoid this, round off sharp corners in your design. Smooth transitions help the laser maintain a consistent speed, resulting in cleaner cuts.
Avoiding Overlapping Lines
Overlapping lines can confuse the laser and lead to duplicate cuts. This wastes time and may damage the material. Carefully inspect your design to ensure no lines overlap. Use your CAD software’s tools to merge or delete redundant lines. A clean design minimizes errors and enhances efficiency.
File Formats Compatible with Laser Cutting Machines
Choosing the right file format is essential for compatibility with your laser cutting machine. Most machines support vector-based formats, as these provide the precision needed for accurate cuts. Here are the most commonly used formats:
- SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics): Ideal for simple designs and widely supported by laser cutting software.
- DXF (Drawing Exchange Format): A popular choice for CAD-based designs, especially in industrial applications.
- AI (Adobe Illustrator): Perfect for intricate designs created in Adobe Illustrator.
Before uploading your file, double-check the machine’s specifications to ensure compatibility. Some machines may require specific settings or file adjustments. By using the correct format, you’ll streamline the cutting process and avoid unnecessary delays.
By focusing on clean vector files, efficient cutting paths, and compatible formats, you can set yourself up for success in laser cutting. These steps not only improve the quality of your work but also make the entire process smoother and more enjoyable. Ready to bring your designs to life? Start with these tips and watch your projects shine!
Troubleshooting and Maintenance of Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines are powerful tools, but like any equipment, they can face issues. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems and maintain your machine ensures smooth operation and extends its lifespan. Let’s dive into the most frequent challenges and how to address them.
Common Issues in Laser Cutting
Inconsistent Cuts
Inconsistent cuts can frustrate you, especially when precision matters. This issue often stems from misaligned optics or a dirty lens. Check the alignment of the laser beam and clean the lens regularly. Dust or debris can scatter the beam, causing uneven results. Also, verify the focus point. If the laser isn’t properly focused, the cut quality will suffer. Adjust the focus to match the material thickness for better performance.
Burn Marks on Steel
Burn marks on steel occur when the laser generates excessive heat. This problem usually happens when the cutting speed is too slow or the laser power is too high. To fix this, increase the cutting speed slightly or reduce the laser power. Using nitrogen as an assist gas can also help. Nitrogen prevents oxidation, leaving cleaner edges. Always test your settings on scrap material before starting a project to avoid unwanted marks.
Machine Overheating
Overheating can damage your laser cutting machine and disrupt your workflow. This issue often arises from prolonged use without proper cooling. Ensure the machine’s cooling system is functioning correctly. Check the coolant levels and clean the cooling unit to prevent blockages. If the machine continues to overheat, give it a break to cool down. Regular maintenance of the cooling system keeps your machine running efficiently.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Cleaning the Cutting Head
The cutting head plays a crucial role in laser cutting. Dirt or residue on the cutting head can affect the laser’s precision. Clean the cutting head after every use. Use a soft cloth and a cleaning solution designed for optical components. Pay special attention to the nozzle and lens. A clean cutting head ensures consistent cuts and prolongs the machine’s life.
Replacing Worn Components
Over time, some parts of your laser cutting machine will wear out. Components like lenses, nozzles, and belts need regular inspection. Replace worn parts immediately to maintain the machine’s performance. Ignoring these issues can lead to poor-quality cuts or even machine failure. Keep spare parts on hand to minimize downtime and keep your projects on track.
When to Call for Professional Support
Sometimes, troubleshooting and maintenance may not solve the problem. If your laser cutting machine shows persistent issues, it’s time to call a professional. Problems like electrical malfunctions or software errors require expert attention. Don’t attempt to fix these on your own, as it could void the warranty or worsen the issue. A professional technician can diagnose and repair the machine, ensuring it operates safely and efficiently.
By addressing common issues, performing regular maintenance, and knowing when to seek professional help, you can keep your laser machines in top condition. This proactive approach not only improves the quality of your cuts but also extends the life of your equipment.
Advanced Tips for Better Results in Laser Cutting
When it comes to laser cutting, achieving professional-grade results often requires more than just basic knowledge. By applying advanced techniques, you can elevate the quality of your cuts and tackle challenging projects with confidence. Let’s explore some expert tips to help you refine your process.
Minimizing Heat-Affected Zones
Heat-affected zones (HAZ) can compromise the integrity and appearance of your steel plates. These zones occur when excessive heat alters the material’s properties near the cut edges. To minimize this effect, focus on controlling the laser’s energy and speed.
Start by adjusting the cutting speed. A faster speed reduces the amount of heat absorbed by the material, which helps limit the size of the HAZ. Pair this with moderate laser power to ensure the beam penetrates the steel without overheating it. For instance, when working with mild steel, avoid prolonged dwell time in one area, as this can lead to excessive heating and damage.
Proper assist gas selection also plays a role. Nitrogen is an excellent choice for reducing oxidation and maintaining clean edges. It prevents additional heat from chemical reactions, unlike oxygen, which can amplify the heat. Additionally, ensure your machine’s focus point is precisely calibrated. A tightly focused beam delivers energy efficiently, reducing unnecessary heat spread.
By fine-tuning these parameters, you can keep the heat-affected zones to a minimum and maintain the structural integrity of your steel plates.
Using Perforation Techniques for Thick Steel
Cutting thick steel plates can be challenging, but perforation techniques offer a practical solution. This method involves creating small holes or perforations along the cutting path before completing the full cut. It’s particularly effective for materials like carbon steel, where stability and precision are crucial.
Pulse lasers with high peak power work best for this technique. They create controlled bursts of energy that penetrate the steel without causing excessive slag formation. Oxygen as an assist gas enhances this process by generating additional heat, making it easier to cut through thick sections. However, balance is key—too much oxygen can lead to burnt edges, so adjust the gas pressure carefully.
Perforation optimization tips include spacing the perforations evenly and ensuring they align with your design. This approach reduces stress on the material and prevents warping. Once the perforations are complete, proceed with the final cut, allowing the laser to follow the pre-drilled path smoothly.
Using this technique not only improves cutting efficiency but also ensures cleaner edges and reduced material waste.
Fine-Tuning for Intricate Designs
Intricate designs demand precision and attention to detail. To achieve flawless results, you need to fine-tune your laser cutting process. Start by preparing clean vector files with well-defined paths. Avoid overlapping lines or unnecessary details that could confuse the laser.
Next, focus on optimizing the kerf width. A narrower kerf allows for more precise cuts, which is essential for detailed patterns. Use a shorter focal length lens to achieve a tighter focus, especially when working with carbon steel. Regularly inspect and clean the cutting head to maintain consistent performance.
Adjusting the cutting speed and power is equally important. Slower speeds give the laser more time to follow complex paths accurately, while lower power levels prevent burn marks on delicate sections. Test your settings on scrap material to ensure they’re suitable for your design.
Lastly, secure the workpiece firmly to the workbed. Movement during the cutting process can lead to inaccuracies, especially in intricate designs. By stabilizing the material, you’ll achieve cleaner cuts and avoid errors.
With these adjustments, you can bring even the most complex designs to life with precision and ease.
Mastering laser cutting for steel plates requires a combination of preparation, precision, and practice. By applying the tips shared in this guide, you can achieve high-quality cuts while improving your cutting quality and overall performance. Regular maintenance ensures your machine operates efficiently, while continuous learning helps you refine your techniques. Start with simple projects, experiment with settings, and don’t hesitate to seek support when needed. With dedication and the right strategies, you’ll unlock the full potential of laser cutting and elevate your results to professional levels.
FAQ
What is laser cutting used for?
Laser cutting is a versatile process that’s widely used across industries. You can use it to cut metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel with precision. It’s also great for creating intricate designs, making it popular in industries like automotive, aerospace, and even art. The high accuracy and speed of laser cutters make them ideal for projects requiring clean edges and detailed patterns.
Can all types of steel be cut with a laser machine?
Not all steel types are suitable for laser cutting. Materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel work best with fiber laser machines. These steels respond well to the laser’s heat, ensuring smooth and precise cuts. However, materials with reflective surfaces or coatings may require special adjustments to avoid damaging the machine.
How thick can a laser cutting machine cut steel plates?
The thickness a laser machine can handle depends on its power and the type of steel. For instance, a high-powered fiber laser can cut carbon steel up to 25mm thick and stainless steel up to 20mm. Thinner plates are easier to cut and produce cleaner results, while thicker plates may need slower speeds and higher power settings.
What assist gases should I use for laser cutting steel?
The choice of assist gas depends on your project’s needs. Oxygen is great for faster cuts and works well with carbon steel, but it can leave an oxide layer on the edges. Nitrogen, on the other hand, produces cleaner, oxidation-free edges, making it ideal for stainless steel. Always match the gas to your material and desired finish.
Why are my laser cuts inconsistent?
Inconsistent cuts often result from misaligned optics, dirty lenses, or incorrect focus settings. Regularly clean the cutting head and check the alignment of the laser beam. Also, ensure the focus point matches the material’s thickness. Testing your setup on scrap material can help identify and fix these issues before starting your project.
How do I prepare my design files for laser cutting?
Start with clean vector files in formats like SVG, DXF, or AI. These files guide the laser along precise paths. Avoid overlapping lines or unnecessary details, as they can confuse the machine. Simplify your design for better results, and always double-check for compatibility with your laser cutter’s software.
What safety precautions should I take when using a laser cutting machine?
Safety is crucial when working with laser machines. Always wear protective gear like goggles and gloves. Ensure proper ventilation to remove fumes and particles. Never look directly at the laser beam, and keep the workspace clean to reduce fire risks. Familiarize yourself with the machine’s emergency stop button for quick action in case of malfunctions.
How can I reduce burn marks on steel during laser cutting?
Burn marks usually occur when the laser power is too high or the cutting speed is too slow. Adjust these settings to find the right balance. Using nitrogen as an assist gas can also help, as it prevents oxidation and leaves cleaner edges. Testing your settings on scrap material can save you from unwanted marks.
What maintenance does a laser cutting machine require?
Regular maintenance keeps your machine running smoothly. Clean the cutting head and lenses after each use to prevent debris buildup. Inspect and replace worn components like nozzles and belts. Check the cooling system to avoid overheating. A well-maintained machine ensures consistent performance and extends its lifespan.
Can I cut intricate designs with a laser machine?
Yes, laser machines excel at cutting intricate designs. To achieve the best results, use a clean vector file and optimize the kerf width for precision. Secure the material firmly to prevent movement during cutting. Adjust the speed and power settings to match the complexity of your design. With the right setup, you can bring even the most detailed patterns to life.
See Also
Mastering Effective Techniques for Laser Cutting Machines
Essential Guidelines for Effective Plasma Cutting Machine Use
Best Practices for Operating a Meat Cutting Machine
