Step-by-Step Guide to Make a Laser Cutting Machine

Learning how to make laser cutting machine can be an exciting and rewarding project. A laser cutting machine is a powerful tool that uses a focused laser beam to cut or engrave materials with incredible precision. It’s widely used in industries like manufacturing, design, and even DIY projects. Building one yourself not only saves money but also allows you to customize it to meet your specific needs. Additionally, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of its functionality. However, safety should always be a top priority. When learning how to make laser cutting machine, it’s essential to take proper precautions, such as wearing protective gear and ensuring the setup is secure. With precision and care, your project will be both successful and fulfilling.
Key Takeaways
- Building your own laser cutting machine can save money and allow for customization to fit your specific needs.
- Gather essential tools and materials beforehand to streamline the assembly process and avoid delays.
- Safety is paramount; always wear protective gear and ensure your workspace is well-ventilated during assembly and operation.
- Understanding the core components, such as the laser source, cutting head, and control system, is crucial for successful assembly and operation.
- Regular maintenance, including cleaning optics, and inspecting wiring, is essential to keep your machine running smoothly and safely.
- Testing and fine-tuning your machine with different materials will help you achieve optimal cutting results and improve overall performance.
- Documenting settings and adjustments during testing can save time and enhance consistency in future projects.
Tools and Materials for How to Make Laser Cutting Machine
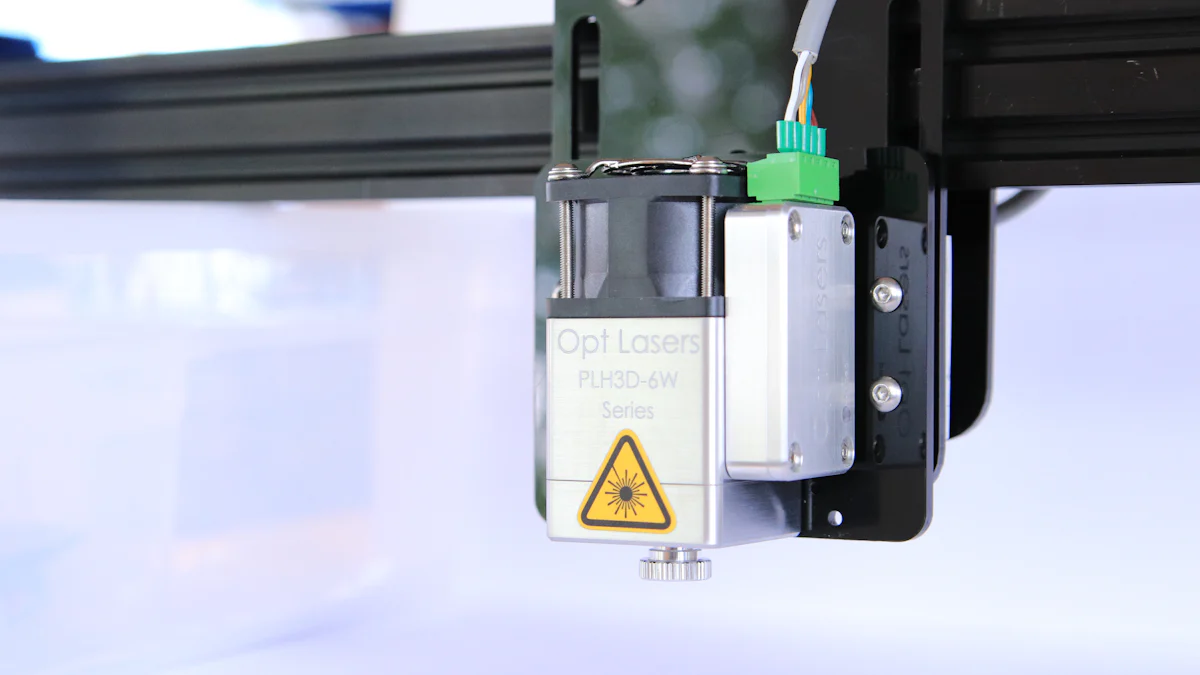
Before diving into the assembly process, you need to gather the right essential tools and materials.
Essential Tools
To build a laser cutting machine, you’ll need a set of tools that help with precise assembly and adjustments. Here’s a list of must-have tools:
- Screwdrivers and Allen Keys: These are crucial for assembling the frame and securing components.
- Multimeter: Use this to check electrical connections and ensure proper wiring.
- Wire Strippers and Cutters: These tools make it easier to handle cables and wires during the setup.
- Drill and Drill Bits: You’ll need these for creating holes in the frame or mounting components.
- Calipers or Measuring Tape: Precision is key, so accurate measurements are essential.
- Soldering Iron: This is necessary for connecting electronic components securely.
- Safety Gear: Always wear safety goggles and gloves to protect yourself during the assembly process.
Having these tools on hand will make the process more efficient and help you avoid unnecessary delays.
Required Materials
The materials you choose will directly impact the performance and durability of your laser cutting machine. Below is a list of the core required materials you’ll need:
- Laser Source: This is the heart of your machine. You can use a laser tube or a laser generator, depending on your budget and requirements.
- Cutting Head and Optics: These components focus the laser beam for precise cutting or engraving.
- Motion System: Includes stepper motors, belts, and rails to control the movement of the laser head.
- Control System: A control board or microcontroller to manage the machine’s operations.
- Frame and Enclosure: Use sturdy materials like aluminum or steel for the frame. The enclosure ensures safety by containing the laser beam.
- Cooling System: A water or air cooling system prevents the laser source from overheating.
- Exhaust System: This removes smoke and fumes generated during cutting.
- Assist Gas System: Helps improve cutting quality by blowing away debris and cooling the material.
- Wires and Connectors: These are essential for connecting all the electronic components.
- Work Table (Bed): Choose a flat and stable surface that supports the materials you’ll cut.
Pro Tip: Before starting, unbox and inspect all components to ensure nothing is missing or damaged. This step will save you from unexpected interruptions later.
By gathering these tools and materials, you’ll be well-prepared to start building your laser cutting machine. Each item plays a vital role in ensuring the machine operates smoothly and delivers precise results.
Core Components of How to Make Laser Cutting Machine

When building a laser cutting machine, understanding its core components is crucial.
Laser Source
The laser source is the powerhouse of your machine. It generates the laser beam that performs the cutting or engraving. You can choose between a laser tube or a fiber laser source, depending on your budget and the materials you plan to work with. A laser tube is more affordable and suitable for beginners, while a fiber laser offers higher precision and durability.
Tip: Ensure the laser source matches the power requirements of your project. For instance, a 40W laser is ideal for light materials like wood or acrylic, while a 100W laser works better for metals.
Proper cooling is essential for the laser source. Overheating can damage it and reduce its lifespan. A water or air cooling system will help maintain optimal performance. Always check the manufacturer’s recommendations for cooling solutions.
Cutting Head
The cutting head is where the magic happens. It directs the laser beam onto the material with precision. This component includes several parts:
- Focusing Lens: Concentrates the laser beam for accurate cutting.
- Nozzle: Guides the assist gas to the cutting area, improving the quality of the cut.
- Protective Window: Shields the internal optics from debris and dust.
- Capacitive Sensor: Maintains the correct distance between the cutting head and the material.
You’ll need to align the cutting head carefully to ensure the laser beam hits the material at the right angle. Misalignment can lead to uneven cuts or damage to the machine. Regular cleaning of the lens and nozzle will also keep the cutting head in top condition.
Motion System
The motion system controls the movement of the cutting head across the work area. It ensures the laser follows the design accurately. This system typically includes:
- Stepper Motors: Drive the movement of the cutting head along the X, Y, and Z axes.
- Linear Guides: Provide smooth and precise motion.
- Belts or Gantry: Transfer the motor’s movement to the cutting head.
Understanding the axis nomenclature is important. The X-axis moves the head horizontally, the Y-axis moves it vertically, and the Z-axis adjusts the height. Before starting, test the motion system to ensure it operates smoothly without jerks or delays. Proper lubrication of the guides and regular maintenance will extend the life of this system.
Pro Tip: Use a CNC control system to manage the motion system. It simplifies the process and ensures consistent results.
By focusing on these core components, you’ll build a laser cutting machine that’s both reliable and efficient. Each part contributes to the overall performance, so take your time during assembly and testing. With the right setup, you’ll achieve professional-grade results.
Control System
The control system acts as the brain of your laser cutting machine.
You’ll typically use a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system or a microcontroller like Arduino or Raspberry Pi. These systems interpret the design files and translate them into commands for the motion system and laser source. Here’s what you need to know:
- Control Board: This is the central hub that connects all electronic components. It processes the instructions and sends signals to the motors and laser.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the control board supports the software you plan to use. Popular options include GRBL, LightBurn, or LaserGRBL.
- Wiring and Connections: Properly connect the control board to the stepper motors, laser source, and power supply. Use labeled wires to avoid confusion during assembly.
- Power Supply: Match the power supply to the voltage and current requirements of your control system. An inadequate power supply can cause malfunctions.
Pro Tip: Test the control system before final assembly. Upload a simple design file and check if the cutting head moves as expected. This step helps identify wiring or configuration issues early.
A well-configured control system ensures your machine operates efficiently and delivers accurate results. Take your time to set it up correctly, as it directly impacts the performance of your laser cutting machine.
Frame and Enclosure
The frame and enclosure provide the structural foundation and safety features for your laser cutting machine. A sturdy frame ensures stability during operation, while the enclosure protects you from the laser beam and debris.
Frame
The frame supports all the components, so it must be durable and rigid. Aluminum extrusions are a popular choice due to their strength and lightweight properties. Steel is another option if you need extra durability. Here’s how to build a reliable frame:
- Material Selection: Use aluminum profiles or steel bars for the frame. These materials resist vibrations and maintain alignment.
- Assembly: Secure the frame using screws, brackets, and corner connectors. Double-check the alignment to ensure the frame is square and level.
- Mounting Points: Add mounting points for the motion system, laser source, and control board. Pre-drill holes to simplify the installation process.
Enclosure
The enclosure enhances safety by containing the laser beam and preventing exposure to harmful fumes. It also keeps dust and debris away from sensitive components. Consider these tips when designing the enclosure:
- Material: Use acrylic sheets, metal panels, or wood for the enclosure. Acrylic is transparent, allowing you to monitor the cutting process.
- Ventilation: Install an exhaust fan or ventilation system to remove smoke and fumes. This step is essential for maintaining air quality.
- Access Points: Add doors or removable panels for easy access to the work area and components. Secure them with latches to prevent accidental openings.
- Safety Features: Include interlocks that shut off the laser when the enclosure is open. This feature adds an extra layer of protection.
Pro Tip: Paint or coat the frame and enclosure to prevent rust and improve aesthetics. A polished look makes your DIY project even more impressive.
By building a strong frame and a secure enclosure, you’ll create a safe and stable environment for your laser cutting machine. These components not only enhance performance but also ensure your safety during operation.
Step-by-Step Instructions for How to Make Laser Cutting Machine
Building your laser cutting machine can feel like a big task, but breaking it into smaller steps makes it manageable. Let’s dive into the process step by step.
Building the Frame
The frame is the backbone of your laser cutting machine. It holds all the components together and ensures stability during operation. Start by selecting a sturdy material like aluminum extrusions or steel bars. Aluminum is lightweight and easy to work with, while steel offers extra durability.
- Cut and Prepare Materials: Measure and cut the frame materials to the required lengths. Use a measuring tape and a saw for precise cuts.
- Assemble the Frame: Connect the pieces using screws, brackets, and corner connectors. Double-check that everything is aligned properly. A square and level frame ensures smooth operation later.
- Add Mounting Points: Drill holes or attach brackets where you’ll mount the motion system, laser source, and control board. Pre-drilling saves time during assembly.
- Secure the Frame: Tighten all screws and bolts to prevent wobbling. A stable frame reduces vibrations, which improves cutting accuracy.
Pro Tip: Paint or coat the frame to protect it from rust and give it a polished look. This step also adds a professional touch to your DIY project.
Installing the Motion System
The motion system allows the laser head to move precisely across the work area. It’s essential for translating your designs into accurate cuts. Here’s how to set it up:
- Attach Linear Guides: Mount the linear guides onto the frame. These guides ensure smooth and precise movement along the X, Y, and Z axes.
- Install Stepper Motors: Secure the stepper motors to their designated spots. These motors drive the movement of the laser head. Make sure they’re firmly attached to avoid misalignment.
- Connect Belts or Gantry: Attach the belts or gantry system to the stepper motors and the laser head. Adjust the tension to ensure smooth motion without slipping.
- Test the Movement: Manually move the laser head along the guides to check for any resistance or jerks. Proper lubrication of the guides can help maintain smooth motion.
Pro Tip: Use a CNC control system, like Raytools Control Systems, for managing the motion system. It simplifies the process and ensures consistent results.
Mounting the Laser Source
The laser source is the heart of your machine. It generates the laser beam that cuts or engraves materials. Follow these steps to mount it correctly:
- Choose the Right Laser Source: Select a laser tube or fiber laser based on your needs. For beginners, a laser tube is more affordable and easier to handle.
- Secure the Laser Source: Mount the laser source onto the frame using brackets or clamps. Ensure it’s stable and aligned with the cutting head.
- Install the Cooling System: Attach a water or air cooling system to prevent the laser source from overheating. Proper cooling extends the lifespan of your laser.
- Align the Laser Beam: Use a target or alignment tool to ensure the laser beam hits the cutting head at the correct angle. Misalignment can lead to poor cutting quality or damage to the machine.
Pro Tip: If you’re using a DSP Laser Controller, you can adjust the laser power intensity directly within the software. This feature makes it easier to fine-tune your machine for different materials.
By completing these steps, you’ll have a solid foundation for your laser cutting machine. Each part of the process plays a critical role in ensuring the machine operates smoothly and delivers precise results. Take your time, double-check your work, and enjoy the satisfaction of building your own laser cutter.
Wiring and Electronics
The wiring and electronics stage is where your laser cutting machine truly comes to life. This step connects all the components, ensuring they work together seamlessly. Precision and organization are key here, as improper wiring can lead to malfunctions or even damage. Let’s break it down into manageable steps.
-
Organize Your Components Lay out all the electronic parts, including the control board, stepper motor drivers, power supply, and laser source. Group related components to avoid confusion during wiring. Use labeled wires to make connections easier to track.
-
Install the Control Board Mount the control board securely onto the frame. This board acts as the brain of your machine, managing the motion system and laser source. Popular options like Raytools Control Systems or Bochu Control Systems offer reliable performance. If you’re looking for advanced features, Bochu provides excellent customization and adaptability.
-
Connect the Stepper Motors Wire the stepper motors to the control board. These motors drive the motion system, so ensure the connections are tight and secure. Follow the manufacturer’s wiring diagram to avoid errors. Test each motor individually to confirm proper movement.
-
Power Supply Setup Connect the power supply to the control board and other components. Match the voltage and current requirements to prevent overloading. Use a multimeter to verify the connections and ensure stable power delivery.
-
Laser Source Wiring Attach the laser source to the control board. If you’re using a DSP Laser Controller, you can adjust the laser power intensity directly through the software. This feature simplifies the process and ensures precise control.
-
Cooling and Exhaust Systems Wire the cooling system to the power supply. A water or air cooling system prevents the laser source from overheating. Also, connect the exhaust system to remove smoke and fumes. Proper ventilation is essential for safe operation.
-
Cable Management Use cable ties or sleeves to organize the wires neatly. Keep them away from moving parts to prevent tangling or damage. A clean setup not only looks professional but also makes troubleshooting easier.
Pro Tip: Double-check all connections before powering on the machine. A small mistake in wiring can lead to significant issues later.
By completing this step carefully, you’ll ensure that your laser cutting machine operates smoothly and efficiently. Take your time, follow the diagrams, and don’t hesitate to test each connection as you go.
Final Assembly
The final assembly is where everything comes together. This step involves integrating all the components, securing them in place, and preparing the machine for its first test run. Let’s wrap up your project with these steps:
-
Secure All Components Double-check that every part is firmly attached to the frame. Tighten screws, brackets, and connectors. A stable setup reduces vibrations and improves cutting accuracy.
-
Install the Enclosure Add the enclosure to your machine. This vital safety feature contains the laser beam and protects you from debris. Use materials like acrylic or metal panels for durability. Include ventilation openings for the exhaust system.
-
Add Safety Features Equip your machine with safety features like emergency stop buttons and interlocks. These features shut off the laser when the enclosure is open, ensuring safe operation. Position the emergency stop button within easy reach.
-
Test the Motion System Power on the machine and test the motion system. Use the control software to move the cutting head along the X, Y, and Z axes. Ensure smooth and precise movement without jerks or delays.
-
Align the Laser Beam Perform a final alignment of the laser beam. Use an alignment tool to ensure the beam hits the cutting head at the correct angle. This step is crucial for achieving accurate cuts.
-
Run a Test Design Upload a simple design file to the control software, such as RDWorks V8 or LightBurn. Perform a test cut on a scrap material to check the machine’s performance. Adjust settings as needed for optimal results.
Pro Tip: Keep a log of your settings during the test run. This record will help you fine-tune the machine for different materials in the future.
With the final assembly complete, your laser cutting machine is ready for action. You’ve built a powerful tool that combines precision, efficiency, and customization. Take pride in your accomplishment and enjoy the endless possibilities it offers.
Software Setup and Configuration
Setting up the software for your laser cutting machine is a crucial step. The right software ensures smooth operation and precise results. This section will guide you through selecting, installing, and testing the software to get your machine up and running.
Choosing the Right Software
The software you choose will act as the command center for your laser cutting machine. It translates your designs into instructions that the machine can follow. Picking the right one depends on your needs and the control system you’ve installed.
Here are some popular options to consider:
- LightBurn: A user-friendly software with powerful design and editing tools. It’s perfect for beginners and professionals alike.
- LaserGRBL: A free and open-source option for those on a budget. It’s great for basic tasks and supports many control boards.
- RDWorks V8: Ideal if you’re using a DSP controller. It offers advanced features for precise control and customization.
Pro Tip: Check the compatibility of the software with your control board before making a decision. Some software works better with specific systems, like GRBL or DSP controllers.
When choosing software, think about your project goals. If you’re new to laser cutting, start with something simple and intuitive. For more complex designs, opt for software with advanced features.
Installing and Configuring the Software
Once you’ve chosen the software, it’s time to install and configure it. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth setup:
-
Download the Software
Visit the official website of your chosen software. Download the latest version to ensure you have access to all the updated features. -
Install the Software
Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions. Most software provides a step-by-step guide during installation. Choose the default settings unless you have specific preferences. -
Connect Your Machine
Plug your laser cutting machine into your computer using a USB cable. Ensure the connection is secure. Some software may require drivers to recognize the machine. Install these drivers if prompted. -
Configure the Settings
Open the software and navigate to the settings menu. Input the specifications of your machine, such as the work area dimensions, laser power, and motion system type. Refer to your control board’s manual for accurate details. -
Test the Connection
Use the software to send a simple command, like moving the laser head. This test confirms that the machine and software are communicating properly.
Pro Tip: Save your configuration settings once everything is set up. This backup will save time if you need to reinstall the software later.
Proper installation and configuration ensure your machine operates efficiently. Take your time during this step to avoid issues down the line.
Testing the Software
Testing the software is the final step before you start using your laser cutting machine. This process ensures everything works as expected and helps you identify any adjustments needed.
-
Create a Simple Design
Use the software to draw a basic shape, like a square or circle. This design will serve as your test file. Keep it simple to focus on functionality rather than complexity. -
Generate G-Code
Convert your design into G-code, the language your machine understands. Most software has a built-in feature for this. Double-check the code to ensure it matches your design. -
Run a Test Cut
Place a scrap material on the work table. Use the software to send the G-code to your machine. Observe the cutting process closely to ensure smooth operation. -
Evaluate the Results
Inspect the cut for accuracy and quality. Look for clean edges and precise dimensions. If you notice any issues, adjust the settings in the software and run another test. -
Fine-Tune the Settings
Experiment with different parameters, like laser power and speed. Fine-tuning these settings helps you achieve the best results for various materials.
Pro Tip: Keep a notebook to record the settings that work best for each material. This reference will save time in future projects.
Testing the software ensures your machine is ready for real projects. It also gives you a chance to familiarize yourself with the software’s features. With everything set up and tested, you’re now equipped to bring your designs to life!
Safety Precautions for How to Make Laser Cutting Machine
Safety should always come first when building and using a laser cutting machine. Whether you're assembling the components, operating the machine, or maintaining it, taking the right precautions will protect you and ensure the machine functions properly. Let’s break it down into three key areas.
During Assembly
When putting your laser cutting machine together, you’ll handle tools, electronics, and potentially hazardous components. Staying cautious during this phase is critical.
- Wear Protective Gear: Always use safety goggles and gloves. Goggles protect your eyes from flying debris, while gloves shield your hands from sharp edges or hot surfaces.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Some materials or adhesives may release fumes during assembly. Proper ventilation keeps the air safe to breathe.
- Handle Electronics Carefully: Double-check all wiring connections before powering up the machine. Use a multimeter to test circuits and avoid short circuits or electrical shocks.
- Secure Components Firmly: Loose parts can cause instability or vibrations. Tighten screws and bolts properly to ensure the frame and other components stay in place.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: If you’re using pre-made parts like a laser tube or control board, stick to the manufacturer’s instructions. These guidelines are designed to ensure safety and compatibility.
Tip: Take your time during assembly. Rushing can lead to mistakes that compromise both safety and performance.
During Operation
Operating a laser cutting machine involves high-powered lasers and moving parts. You need to stay alert and follow strict safety measures to avoid accidents.
- Never Look Directly at the Laser Beam: Even a brief exposure can damage your eyes. Always keep the enclosure closed while the machine is running.
- Use the Enclosure: The enclosure contains the laser beam and prevents exposure to harmful light or debris. Ensure it’s securely closed before starting the machine.
- Monitor the Machine: Never leave the machine unattended during operation. Materials can catch fire, or the machine might malfunction.
- Ventilate the Workspace: Cutting certain materials, like acrylic or wood, produces smoke and fumes. Use an exhaust system or open windows to maintain air quality.
- Keep a Fire Extinguisher Nearby: Lasers generate heat, which can ignite flammable materials. A fire extinguisher provides a quick way to handle emergencies.
- Avoid Loose Clothing: Loose sleeves or jewelry can get caught in moving parts. Wear fitted clothing and tie back long hair.
Pro Tip: Create a checklist of safety steps to follow before every use. This habit ensures you don’t overlook any critical precautions.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance keeps your laser cutting machine running smoothly and safely. Neglecting upkeep can lead to malfunctions or even accidents.
- Clean the Optics: Dust or debris on the lens and mirrors can affect the laser’s performance. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to clean these components regularly.
- Inspect the Wiring: Check for frayed wires or loose connections. Replace damaged wires immediately to prevent electrical hazards.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply lubricant to the linear guides and belts to reduce wear and ensure smooth motion.
- Test the Cooling System: Overheating can damage the laser source. Regularly inspect the cooling system and refill water or replace air filters as needed.
- Check the Exhaust System: Ensure the exhaust fan is working properly to remove fumes. Clean or replace filters to maintain efficiency.
- Update Software: If your control software offers updates, install them to improve functionality and security.
Advice from Experts: Engineers recommend creating a maintenance schedule. Regular inspections and tune-ups maximize the machine’s lifespan and performance.
By following these safety precautions, you’ll protect yourself and keep your laser cutting machine in top condition.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Initial Testing
Once your laser cutting machine is fully assembled, it’s time to put it to the test. This step ensures that all components work together as expected. Start with a simple approach to verify the machine’s basic functionality.
-
Power On the Machine
Turn on the power supply and ensure all systems, including the control board, laser source, and motion system, activate correctly. Listen for unusual sounds or vibrations that might indicate loose parts. -
Test the Motion System
Use your software to move the laser head along the X, Y, and Z axes. Check for smooth and precise movements. If the head jerks or stalls, inspect the belts, linear guides, and stepper motors for alignment or tension issues. -
Align the Laser Beam
Perform a beam alignment test. Use a piece of heat-sensitive paper or a target to confirm that the laser beam hits the cutting head’s focal point. Misalignment can lead to poor cutting results or damage to the optics. -
Run a Simple Design
Upload a basic design, like a square or circle, into your software. Use low power settings to perform a test cut on scrap material. Observe the cutting process and inspect the results for accuracy and clean edges.
Tip: Keep a notebook handy to record any observations or adjustments you make during this phase. This log will help you track progress and troubleshoot effectively.
Initial testing helps you identify potential issues early. Take your time and address any problems before moving on to more complex tasks.
Common Issues and Fixes
During testing, you might encounter some common problems. Don’t worry—most of these issues have straightforward solutions. Here’s a quick guide to troubleshooting:
-
Laser Beam Misalignment
If the laser doesn’t hit the focal point, adjust the mirrors and focusing lens. Use alignment tools or follow the manufacturer’s instructions for precise calibration. -
Uneven Cuts or Engravings
Uneven results often stem from improper focus or unstable materials. Double-check the cutting head’s distance from the material and ensure the work table is level. -
Stepper Motors Not Moving
If the motion system doesn’t respond, inspect the wiring connections to the stepper motors and control board. A multimeter can help you verify electrical continuity. -
Overheating Laser Source
Overheating usually indicates a problem with the cooling system. Check for blockages in water or air cooling lines and ensure the system operates efficiently. -
Software Connection Issues
If the software fails to communicate with the machine, confirm that the USB cable is securely connected. Update drivers or reinstall the software if necessary.
Pro Tip: Refer to your software’s user manual or online forums for additional troubleshooting tips. Communities for tools like LightBurn or RDWorks V8 often provide valuable insights.
Addressing these issues promptly ensures your machine operates smoothly. Regular maintenance also helps prevent recurring problems.
Fine-Tuning the Machine
Fine-tuning takes your laser cutting machine from functional to exceptional. This step optimizes performance for precise and consistent results.
-
Adjust Laser Power and Speed
Experiment with different power and speed settings for various materials. For instance, wood may require lower power but slower speed, while acrylic might need higher power. Use your software’s settings to make these adjustments. -
Optimize Focus
The laser’s focus directly impacts cutting quality. Use a focus gauge or test cuts to find the optimal focal length for each material. Adjust the cutting head height accordingly. -
Calibrate the Motion System
Ensure the stepper motors and belts move the laser head accurately. Run calibration tests using grid patterns or ruler guides in your software. Adjust the tension of belts or gantry systems if needed. -
Test Advanced Features
Explore your software’s advanced tools, like nesting algorithms or vector-based design compatibility. These features help you maximize material usage and create intricate designs. -
Document Settings
Keep a record of the best settings for each material. This reference saves time and ensures consistent results in future projects.
Advice: Software like LightBurn or CorelDRAW offers powerful design and layout tools. Familiarize yourself with these features to unlock your machine’s full potential.
Fine-tuning transforms your laser cutter into a precision tool. With patience and practice, you’ll achieve professional-grade results every time.
Building your own laser cutting machine is a rewarding journey. You’ve learned how to assemble the frame, install the motion system, wire the electronics, and configure the software. Each step brings you closer to creating a powerful tool tailored to your needs. Remember, safety is key—wear protective gear, monitor your workspace, and maintain your machine regularly. Completing this project not only saves money but also gives you a sense of accomplishment. Share your experiences or ask questions in the comments. Your insights could inspire others to start their own DIY laser cutting adventure!
FAQ
What materials can I cut with a DIY laser cutting machine?
You can cut a variety of materials, depending on the power of your laser. Common options include wood, acrylic, leather, and fabric. For metals, you’ll need a higher-powered laser, such as a fiber laser. Always check the material’s compatibility with your machine to avoid damage or poor results.
Tip: Avoid cutting PVC or other materials that release harmful fumes when exposed to a laser.
How do I maintain my laser cutting machine?
Regular maintenance keeps your machine running smoothly and safely. Clean the optics, such as the lens and mirrors, to remove dust and debris. Lubricate the motion system to ensure smooth movement. Inspect the wiring and cooling system for any signs of wear or damage.
Remember: Proper maintenance not only extends the life of your machine but also ensures safe operation.
Why is my laser not cutting evenly?
Uneven cuts often result from improper focus or misalignment. Check the focal length of the laser and ensure the cutting head is at the correct height. Also, inspect the work table to confirm it’s level. If the issue persists, clean the optics and test the alignment of the laser beam.
Pro Tip: Fine-tune the laser’s power and speed settings for the material you’re working with to achieve cleaner cuts.
Can I use any software with my laser cutting machine?
Popular options like LightBurn, LaserGRBL, and RDWorks V8 work well with most DIY setups. Before choosing software, confirm it supports your laser cutting machine and offers the features you need.
Advice: Start with user-friendly software if you’re a beginner. Advanced tools can be explored as you gain experience.
How do I align the laser beam?
Aligning the laser beam is crucial for accurate cuts. Use an alignment tool or heat-sensitive paper to check if the beam hits the focal point of the cutting head. Adjust the mirrors and focusing lens until the beam is perfectly aligned.
Quick Tip: Perform alignment tests regularly, especially after moving the machine or replacing components.
What safety precautions should I follow during operation?
Always wear protective goggles to shield your eyes from the laser beam. Keep the enclosure closed while the machine is running. Ensure proper ventilation to remove smoke and fumes. Never leave the machine unattended during operation, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
Safety First: Loose clothing and jewelry can pose risks. Wear fitted attire and tie back long hair.
How do I fine-tune my machine for different materials?
Adjust the laser’s power, speed, and focal length based on the material’s thickness and type. For example, cutting thicker materials may require slower speeds and higher power. Test on scrap pieces to find the optimal settings before starting your project.
Did You Know? Fine-tuning ensures optimal results and reduces material waste.
What should I do if my machine overheats?
Overheating usually indicates an issue with the cooling system. Check for blockages in water or air cooling lines. Ensure the cooling system operates efficiently and refill water or replace filters as needed. Regularly inspect the system to prevent overheating.
Important: Overheating can damage the laser source, so address this issue promptly.
Can I upgrade my DIY laser cutting machine later?
Yes, you can upgrade components like the laser source, control board, or motion system to improve performance. For example, switching to a higher-powered laser allows you to cut thicker materials. Upgrading the software or adding advanced features like auto-focus can also enhance functionality. How much laser cutting machine cost can also enhance functionality.
Pro Tip: Plan your upgrades based on your future project needs and budget.
How do I troubleshoot common issues?
Start by identifying the problem. For motion issues, check the stepper motors and belts. If the laser isn’t cutting properly, inspect the optics and alignment. For software-related problems, ensure the machine is connected correctly and the drivers are updated. Address each issue systematically.
Helpful Hint: Keep a troubleshooting log to track recurring problems and their solutions.
See Also
Comprehensive Instructions for Operating a Hair Clipper
Tips for Optimal Use of Laser Cutting Equipment
Understanding the Functionality of CNC Laser Cutters
